Git & GitHub Cheatsheet for Beginners

In the fast-paced world of software development, mastering version control is essential. Git, a distributed version control system, and GitHub, a cloud-based hosting service for Git repositories, are fundamental tools for developers. Whether you’re an engineering student or a budding developer, understanding these tools can significantly enhance your workflow.
This comprehensive cheatsheet is designed to guide beginners through the core concepts and commands of Git and GitHub, providing you with the knowledge to manage your code efficiently.
What is Git?
Git is a distributed version control system that tracks changes in source code during software development. Unlike centralized version control systems, Git allows each developer to have a local copy of the entire repository, enabling them to work offline and commit changes independently.
What is GitHub?
GitHub is a cloud-based platform that hosts Git repositories, providing a web interface to manage and collaborate on projects. It offers features like pull requests, issues, and actions, facilitating team collaboration and continuous integration.
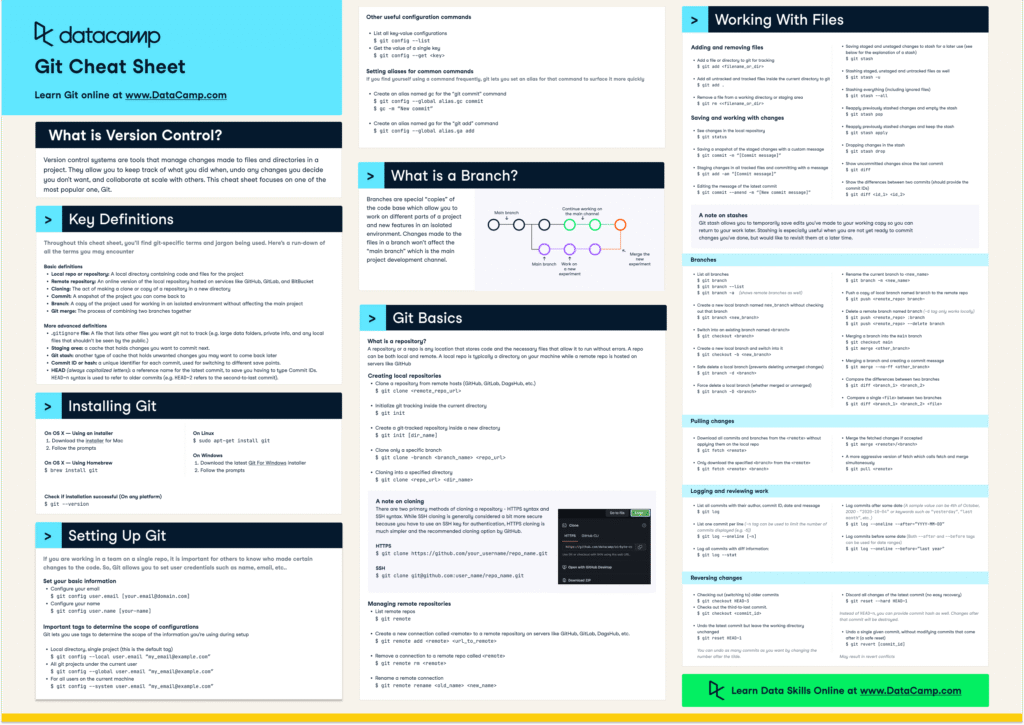
Setting Up Git
Before you can start using Git, you need to install and configure it:
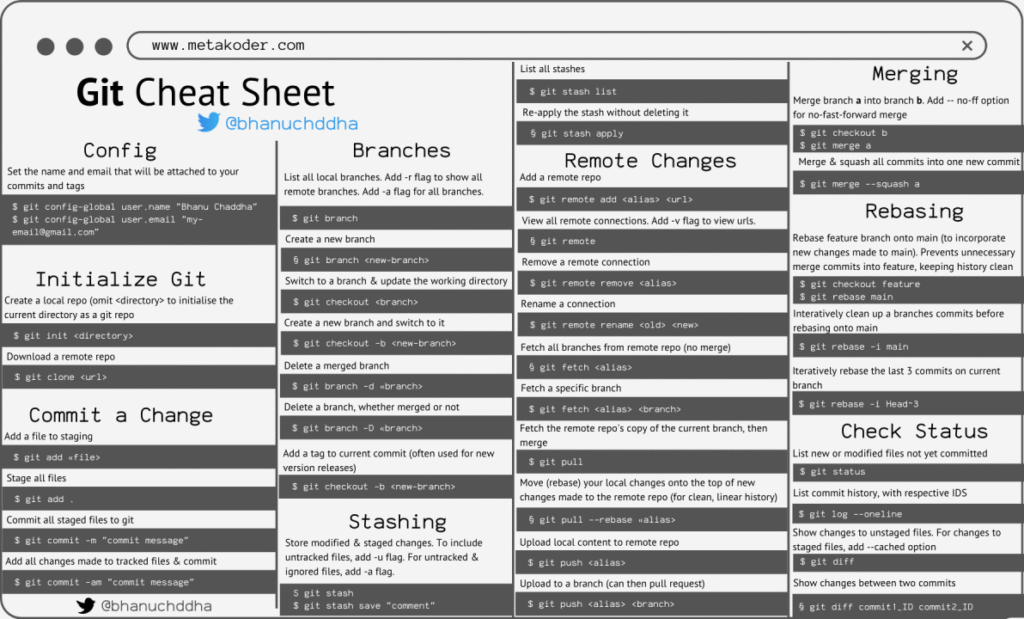
Installation
- Windows: Download the Git installer from the official website and follow the installation prompts.
- macOS: Use Homebrew:
brew install git - Linux: Use your package manager, e.g.,
sudo apt-get install gitfor Ubuntu.
Configuration
Set your user name and email to associate your commits with your identity:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "youremail@example.com"
Verify your configuration:
git config --list
Basic Git Commands
Here are some essential Git commands every beginner should know:
Repository Initialization
git init— Initializes a new Git repository.git clone <repository-url>— Clones an existing repository.
Staging and Committing Changes
git add <file>— Stages a file for commit.git commit -m "message"— Commits the staged changes with a message.git status— Displays the status of the working directory and staging area.git diff— Shows changes between commits, commit and working tree, etc.
Viewing Commit History
git log— Shows the commit history.git log --oneline— Shows a simplified commit history.

Working with Branches
Branches allow you to work on different versions of a repository simultaneously.
Creating and Switching Branches
git branch <branch-name>— Creates a new branch.git checkout <branch-name>— Switches to the specified branch.git checkout -b <branch-name>— Creates and switches to a new branch.
Merging Branches
git merge <branch-name>— Merges the specified branch into the current branch.
Deleting Branches
git branch -d <branch-name>— Deletes the specified branch.
Collaborating with GitHub
GitHub enhances Git by providing a platform for collaboration.
Connecting to a Remote Repository
git remote add origin <repository-url>— Adds a remote repository.
Pushing Changes
git push origin <branch-name>— Pushes changes to the remote repository.
Pulling Changes
git pull origin <branch-name>— Fetches and merges changes from the remote repository.
Fetching Changes
git fetch origin— Fetches changes from the remote repository without merging.
Best Practices
- Commit Often: Make small, frequent commits with clear messages.
- Use Branches: Develop features in separate branches to keep the main branch stable.
- Pull Before Pushing: Always pull the latest changes before pushing your own.
- Write Descriptive Commit Messages: Clearly explain the purpose of each commit.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Merge Conflicts: If a merge conflict occurs, Git will mark the conflicted areas in the files. Resolve the conflicts manually, then stage and commit the changes.
- Undoing Changes: Use
git checkout -- <file>to discard changes in a file, orgit reset --hardto reset the working directory to the last commit. - Viewing Differences: Use
git diffto see what changes have been made compared to the last commit.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between Git and GitHub?
Git is a version control system that tracks changes in files, while GitHub is a platform that hosts Git repositories and facilitates collaboration.
Q2: How do I undo a commit in Git?
To undo the last commit, use git reset --soft HEAD~1 to keep changes staged, or git reset --hard HEAD~1 to discard changes.
Q3: What is a pull request?
A pull request is a way to propose changes to a repository. It allows others to review and discuss the changes before merging them into the main branch.
Q4: How can I ignore certain files in Git?
Create a .gitignore file in the root of your repository and list the files or directories you want to ignore.
Q5: Can I use Git without GitHub?
Yes, Git can be used locally without GitHub. However, GitHub provides a platform for remote collaboration and backup.
Conclusion
Mastering Git and GitHub is a valuable skill for any developer. By understanding the basic commands and workflows, you can manage your code efficiently and collaborate effectively with others. Remember to practice regularly and follow best practices to become proficient in version control.
For more resources and practice exercises, consider exploring online platforms like Codecademy or freeCodeCamp. Additionally, GitHub’s own documentation provides in-depth tutorials and guides.
[YOUTUBE VIDEO PLACEHOLDER — Search YouTube for: “Git and GitHub for Beginners Tutorial”]
Call to Action:
Ready to dive deeper into version control? Check out our other cheatsheets and resources to enhance your development skills.
Author Profile
- At Learners View, we're passionate about helping learners make informed decisions. Our team dives deep into online course platforms and individual courses to bring you honest, detailed reviews. Whether you're a beginner or a lifelong learner, our insights aim to guide you toward the best educational resources available online.
Latest entries
 UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes
UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)
UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)