C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax
C++ is one of the most widely used programming languages in engineering, competitive programming, and software development. For engineering students, remembering all syntax, concepts, and libraries during exams or interviews can feel overwhelming. That’s where a C++ programming cheatsheet becomes invaluable.
This guide provides a concise yet complete revision of C++ syntax, Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) concepts, and the Standard Template Library (STL). Think of it as your one-stop quick revision notes before coding exams, viva, or placement tests.

Why Use a C++ Cheatsheet?
- Saves revision time before exams or coding contests
- Covers important OOP principles (Inheritance, Polymorphism, Abstraction, Encapsulation)
- Provides ready-to-use STL functions and syntax
- Helps during lab practicals and viva
- Ideal for placements and coding interviews
Basic C++ Syntax Cheatsheet
Structure of a C++ Program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello, World!";
return 0;
}
Key points:
#include <iostream>→ Input/Output stream headerusing namespace std;→ Avoids writingstd::repeatedlyint main()→ Entry point of every programcout→ Prints outputcin→ Takes input
Data Types in C++
- int → integers
- float → decimal values
- double → higher precision decimals
- char → single character
- string → sequence of characters
- bool → true/false
Variables and Constants
int a = 10;
const float PI = 3.14;
constkeyword makes a variable unchangeable.- Variables should be initialized before use.
Operators in C++
- Arithmetic:
+,-,*,/,% - Relational:
==,!=,<,>,<=,>= - Logical:
&&,||,! - Bitwise:
&,|,^,~,<<,>>
Control Structures Cheatsheet
If-Else Statement
if (x > 0) {
cout << "Positive";
} else {
cout << "Non-positive";
}
Switch Case
switch (choice) {
case 1: cout << "One"; break;
case 2: cout << "Two"; break;
default: cout << "Invalid";
}
Loops
- For loop
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
cout << i << " ";
}
- While loop
while(x > 0) {
cout << x;
x--;
}
- Do-while loop
do {
cout << x;
x--;
} while(x > 0);
Functions in C++
Syntax
return_type functionName(parameters) {
// code
}
Example:
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
- Function Overloading
Two or more functions with the same name but different parameters.
int add(int a, int b);
float add(float a, float b);
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts Cheatsheet
OOP is the backbone of C++. Let’s quickly revise its four pillars.
1. Encapsulation
Wrapping data and methods into a single unit (class).
class Student {
private:
int marks;
public:
void setMarks(int m) { marks = m; }
int getMarks() { return marks; }
};
2. Inheritance
Reusing properties and methods from another class.
class Animal {
public:
void eat() { cout << "Eating"; }
};
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
void bark() { cout << "Barking"; }
};
Types of Inheritance:
- Single
- Multiple
- Multilevel
- Hierarchical
- Hybrid
3. Polymorphism
- Compile-time (Function Overloading, Operator Overloading)
- Runtime (Virtual Functions)
class Shape {
public:
virtual void draw() { cout << "Drawing shape"; }
};
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
void draw() override { cout << "Drawing circle"; }
};
4. Abstraction
Hiding implementation details and showing only necessary features.
class Abstract {
virtual void display() = 0; // Pure virtual function
};
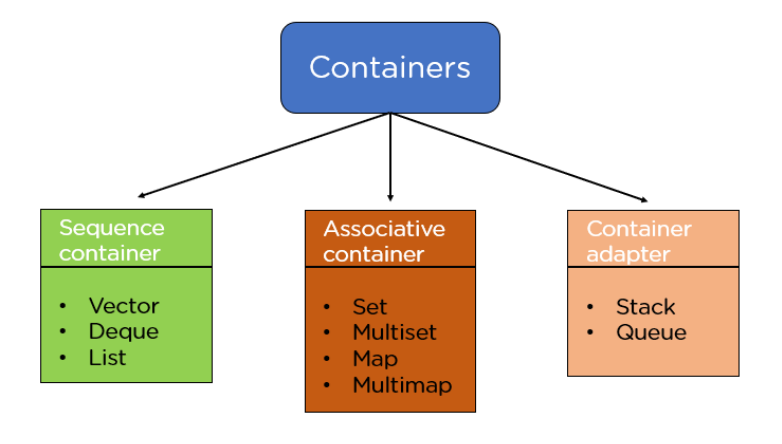
Standard Template Library (STL) Cheatsheet
The STL provides ready-to-use data structures and algorithms. It has four major components:
- Algorithms
- Containers
- Functions
- Iterators
Common Containers
Vector
#include <vector>
vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3};
v.push_back(4);
for(int i : v) cout << i << " ";
Stack
#include <stack>
stack<int> s;
s.push(10);
s.push(20);
cout << s.top(); // 20
s.pop();
Queue
#include <queue>
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
cout << q.front(); // 1
Priority Queue
#include <queue>
priority_queue<int> pq;
pq.push(30);
pq.push(10);
pq.push(20);
cout << pq.top(); // 30 (max heap)
Map
#include <map>
map<int, string> m;
m[1] = "One";
m[2] = "Two";
Useful STL Functions
sort(v.begin(), v.end());→ Sort vectorreverse(v.begin(), v.end());→ Reverse orderfind(v.begin(), v.end(), x);→ Search elementcount(v.begin(), v.end(), x);→ Count occurrencesmax_element(v.begin(), v.end());→ Find max
Exception Handling in C++
try {
int x = 0;
if(x == 0) throw "Division by zero!";
} catch(const char* msg) {
cout << msg;
}
File Handling Cheatsheet
#include <fstream>
ofstream fout("test.txt");
fout << "Hello File!";
fout.close();
ifstream fin("test.txt");
string line;
while(getline(fin, line)) {
cout << line;
}
fin.close();
C++ Exam & Placement Tips
- Revise OOP pillars thoroughly
- Practice STL-based coding problems
- Be confident with pointers and memory allocation
- Review common syntax (switch, loops, functions)
- For placements, practice LeetCode, HackerRank, Codeforces problems
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. What is the best way to revise C++ before exams?
Use a C++ cheatsheet covering syntax, OOP, and STL. Practice 2–3 coding problems daily for confidence.
Q2. What are the four main OOP concepts in C++?
Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Abstraction.
Q3. Which STL containers are most important for placements?
Vectors, Maps, Sets, Queues, and Priority Queues are frequently used in coding interviews.
Q4. Is STL allowed in coding competitions?
Yes, STL is allowed in most coding contests like Codeforces, CodeChef, and LeetCode.
Q5. How is C++ different from C in terms of OOP?
C is procedural, while C++ supports Object-Oriented Programming with classes and objects.
Conclusion
C++ is not just an academic subject but a powerful language used in real-world software, system design, and competitive coding. With this C++ cheatsheet on syntax, OOP concepts, and STL, you now have a quick reference guide to boost your exam preparation and placement readiness.
Use this as a last-minute revision sheet to quickly brush up concepts, avoid silly mistakes, and perform confidently in labs, exams, and interviews.
Author Profile
- At Learners View, we're passionate about helping learners make informed decisions. Our team dives deep into online course platforms and individual courses to bring you honest, detailed reviews. Whether you're a beginner or a lifelong learner, our insights aim to guide you toward the best educational resources available online.
Latest entries
 UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes
UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)
UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)







