Operating System Cheatsheet – Process, Scheduling, Memory Management

Introduction
The Operating System (OS) is one of the most important subjects in computer science and engineering. Whether you are preparing for university exams, coding interviews, or placement tests, OS concepts like process management, CPU scheduling, and memory management form the backbone of system programming and computer fundamentals.
In this comprehensive cheatsheet, we’ll simplify these concepts into easy-to-understand revision notes. You’ll learn about process lifecycle, different scheduling algorithms, memory allocation techniques, and more — all explained in a way that’s perfect for last-minute revision.
Let’s dive in.
What is an Operating System?
An Operating System (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and provides an interface for users and applications.
Functions of an Operating System
- Process Management – Handling process creation, scheduling, and termination.
- Memory Management – Allocating and deallocating memory efficiently.
- File Management – Organizing and controlling file access.
- Device Management – Managing input/output devices.
- Security & Protection – Protecting data and ensuring safe execution.
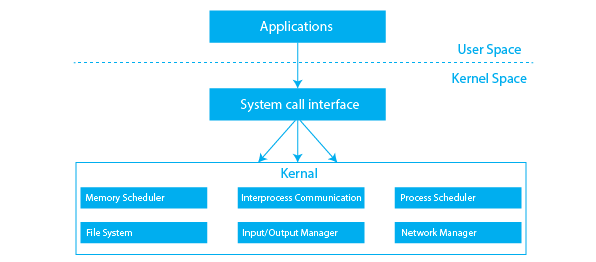
Process Management Cheatsheet
What is a Process?
A process is a program in execution. It includes the program code, data, resources, and the current state of execution.
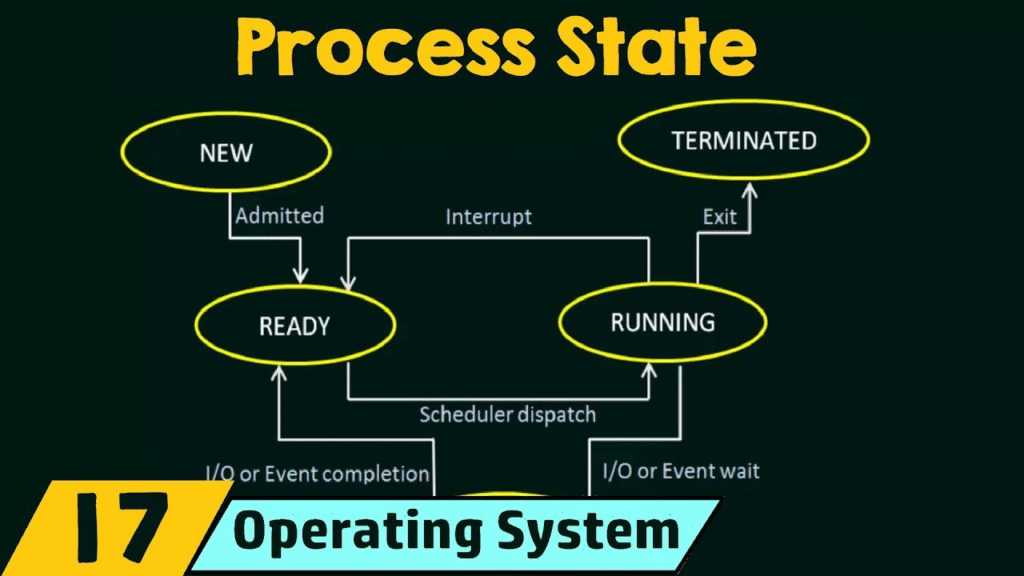
Process States
A process can exist in different states during its execution:
- New – Process is being created.
- Ready – Process is waiting for CPU allocation.
- Running – Process is being executed by the CPU.
- Waiting (Blocked) – Process is waiting for an event (I/O).
- Terminated – Process has finished execution.
Process Control Block (PCB)
The PCB is a data structure that stores information about a process, such as:
- Process ID
- Program Counter
- CPU Registers
- Scheduling Information
- Memory Management Information
CPU Scheduling Cheatsheet
What is CPU Scheduling?
CPU scheduling is the method by which the OS decides which process will be executed by the CPU when multiple processes are ready.
Scheduling Criteria
- CPU Utilization – Keep CPU as busy as possible.
- Throughput – Number of processes completed per unit time.
- Turnaround Time – Time taken to complete a process.
- Waiting Time – Time spent waiting in the ready queue.
- Response Time – Time until the process starts responding.
Types of Scheduling Algorithms
1. First Come, First Serve (FCFS)
- Processes are executed in the order they arrive.
- Simple but may cause convoy effect.
2. Shortest Job Next (SJN) or Shortest Job First (SJF)
- Process with the shortest burst time is scheduled first.
- Can be preemptive (Shortest Remaining Time First) or non-preemptive.
3. Round Robin (RR)
- Each process gets a fixed time quantum.
- Fair for all processes but overhead of context switching.
4. Priority Scheduling
- Each process has a priority value.
- High-priority processes are executed first.
- May cause starvation, solved by aging.
5. Multilevel Queue Scheduling
- Processes are divided into multiple queues (system, interactive, batch, etc.).
- Each queue has its own scheduling algorithm.
Memory Management Cheatsheet
What is Memory Management?
Memory management is the function of an OS that handles allocation and deallocation of memory spaces.
Memory Management Techniques
1. Contiguous Allocation
- Fixed Partitioning – Memory is divided into fixed partitions.
- Dynamic Partitioning – Memory partitions are created dynamically.
2. Non-Contiguous Allocation
- Paging – Memory is divided into fixed-size blocks (pages).
- Segmentation – Memory is divided into variable-sized segments.
- Paged Segmentation – Combination of paging and segmentation.
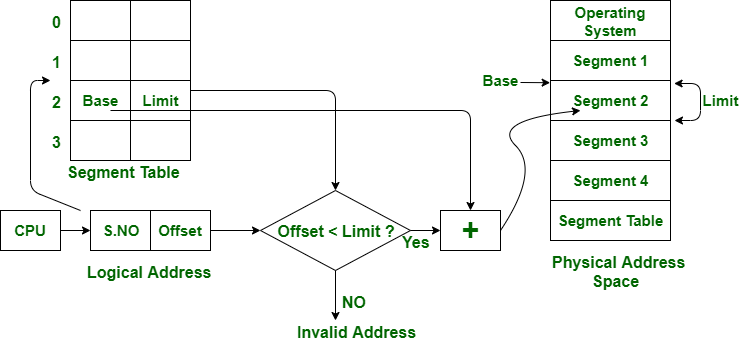
Virtual Memory
- Allows execution of processes not completely in memory.
- Uses demand paging and page replacement algorithms.
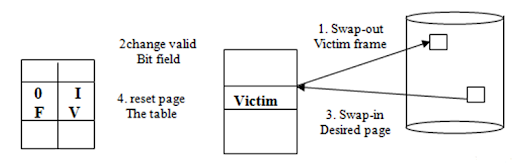
Page Replacement Algorithms
- FIFO (First-In-First-Out)
- Oldest page is replaced first.
- LRU (Least Recently Used)
- Replaces the page that hasn’t been used for the longest time.
- Optimal Page Replacement
- Replaces the page that will not be used for the longest future period.
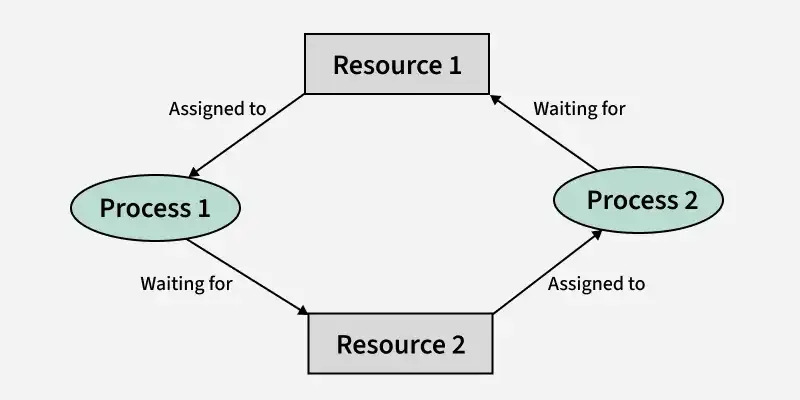
Deadlock in Operating System (Quick Cheatsheet)
What is Deadlock?
A deadlock is a situation where two or more processes are waiting indefinitely for resources held by each other.
Necessary Conditions for Deadlock (Coffman’s Conditions)
- Mutual Exclusion
- Hold and Wait
- No Preemption
- Circular Wait
Deadlock Handling Techniques
- Prevention – Eliminate one of the conditions.
- Avoidance – Use algorithms like Banker’s Algorithm.
- Detection & Recovery – Detect deadlock and restart processes.
Cheatsheet Summary (Quick Notes for Exams)
- Process States: New, Ready, Running, Waiting, Terminated.
- Scheduling Algorithms: FCFS, SJF, Round Robin, Priority, Multilevel Queue.
- Memory Management: Paging, Segmentation, Virtual Memory, Page Replacement.
- Deadlock: 4 conditions, prevention & avoidance strategies.
This summary helps you revise entire OS concepts in 5 minutes before an exam.
FAQs on Operating System Cheatsheet
Q1. What is the difference between process and thread?
A process is an independent program in execution, while a thread is a lightweight unit of execution within a process.
Q2. Which CPU scheduling algorithm is best for time-sharing systems?
Round Robin (RR) is best for time-sharing systems because it ensures fairness by allocating equal CPU time.
Q3. What is the difference between paging and segmentation?
Paging divides memory into fixed-size blocks, while segmentation divides it into variable-sized segments based on logical divisions like functions and data.
Q4. What is thrashing in operating systems?
Thrashing occurs when the system spends most of its time swapping pages in and out of memory instead of executing processes.
Q5. How do operating systems prevent deadlock?
Deadlock can be prevented by avoiding one of Coffman’s conditions, using algorithms like Banker’s Algorithm, or preempting resources.
Conclusion
The Operating System is the heart of computer science. For engineering students, mastering concepts like process scheduling, memory management, and deadlocks is crucial for exams and interviews.
This cheatsheet simplifies these concepts into quick, scannable notes — helping you save time and revise effectively. Whether you’re preparing for semester exams or placement tests, this guide will serve as your go-to OS revision resource.
Author Profile
- At Learners View, we're passionate about helping learners make informed decisions. Our team dives deep into online course platforms and individual courses to bring you honest, detailed reviews. Whether you're a beginner or a lifelong learner, our insights aim to guide you toward the best educational resources available online.
Latest entries
 UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes
UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)
UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)







