Cloud Computing Cheatsheet – Basics, Services, Architecture

Introduction
Cloud computing has become one of the most important topics in modern computer science and engineering. Whether you’re preparing for a BTech exam, a technical interview, or a placement test, understanding the fundamentals of cloud computing is essential.
This Cloud Computing Cheatsheet is designed specifically for engineering students who want concise, easy-to-understand notes for quick revision. Here, you’ll learn:
- What cloud computing is and why it matters
- The three main service models: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
- Types of cloud deployment models
- Cloud computing architecture
- Advantages, challenges, and applications of cloud computing
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear grasp of cloud computing basics in an exam-friendly, revision-focused format.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services (servers, storage, networking, databases, software, analytics, etc.) over the internet (“the cloud”) instead of using local servers or personal devices.
In simple terms:
- Instead of buying expensive hardware and software, you can use them on-demand through the cloud.
- You pay only for what you use, similar to how we pay for electricity or water.
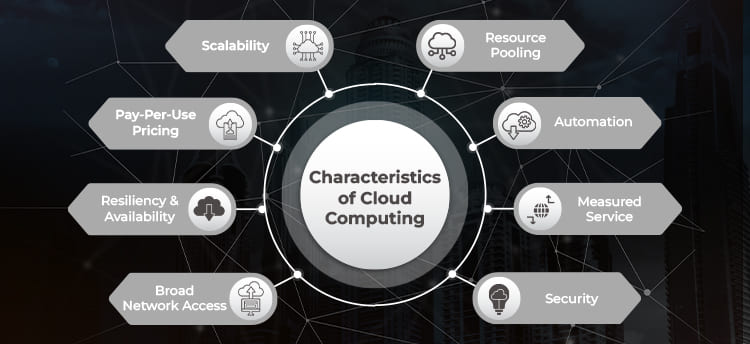
Key Features of Cloud Computing:
- On-demand self-service
- Broad network access
- Resource pooling
- Rapid elasticity (scaling up or down)
- Measured service (pay-as-you-go model)
Why is Cloud Computing Important?
Cloud computing powers everything from social media to online learning platforms, e-commerce websites, and enterprise IT systems. For students, it’s important because:
- It appears in BTech Computer Science and IT exams.
- Cloud-related skills are highly valued in placements and job interviews.
- Many real-world applications (Netflix, Google Drive, AWS, Microsoft Azure) run on the cloud.
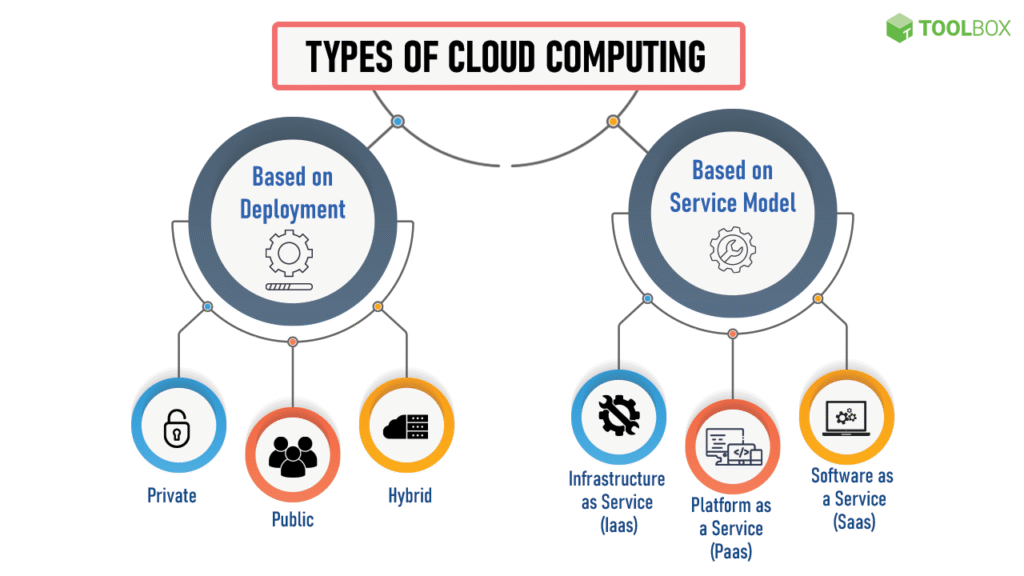
Cloud Computing Service Models
Cloud services are typically divided into three models. Remember the acronym SPI (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS) for exams.
1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- Users get access to servers, storage, and networking without managing physical hardware.
Examples: Amazon Web Services (EC2), Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine
Best for: Companies needing flexible infrastructure.
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- Provides a platform with operating systems, development tools, databases so developers can build applications without managing infrastructure.
- Developers focus on coding while the cloud provider manages the backend.
Examples: Google App Engine, Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Services
Best for: Application development and testing.
3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Provides ready-to-use software applications over the internet.
- No installation or maintenance is needed; users just log in and use the service.
Examples: Gmail, Google Docs, Microsoft Office 365, Zoom
Best for: End users who need software access.
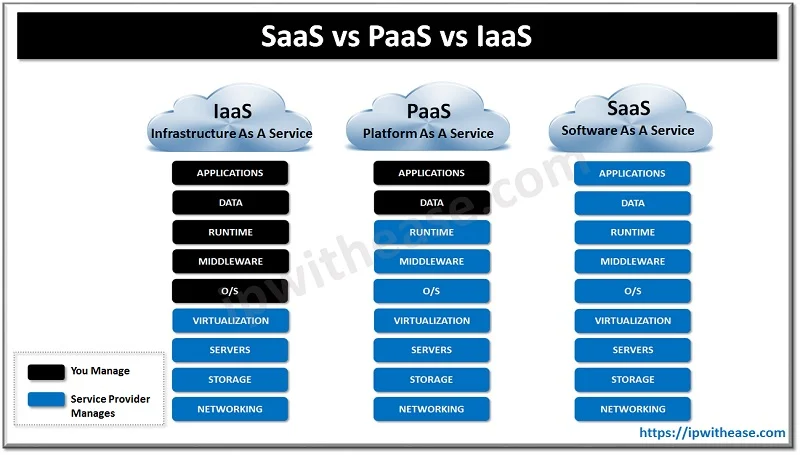
Comparison Table: IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
| Feature | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access Level | Infrastructure | Development platform | Software applications |
| Users | IT admins, developers | Developers | End users |
| Examples | AWS EC2, Azure VMs | Google App Engine, Heroku | Gmail, Office 365, Dropbox |
Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud can be deployed in different ways depending on business or academic needs:
- Public Cloud – Services offered over the public internet (AWS, GCP, Azure).
- Private Cloud – Exclusive use by a single organization.
- Hybrid Cloud – Combination of public and private cloud.
- Community Cloud – Shared by organizations with similar goals (e.g., government).
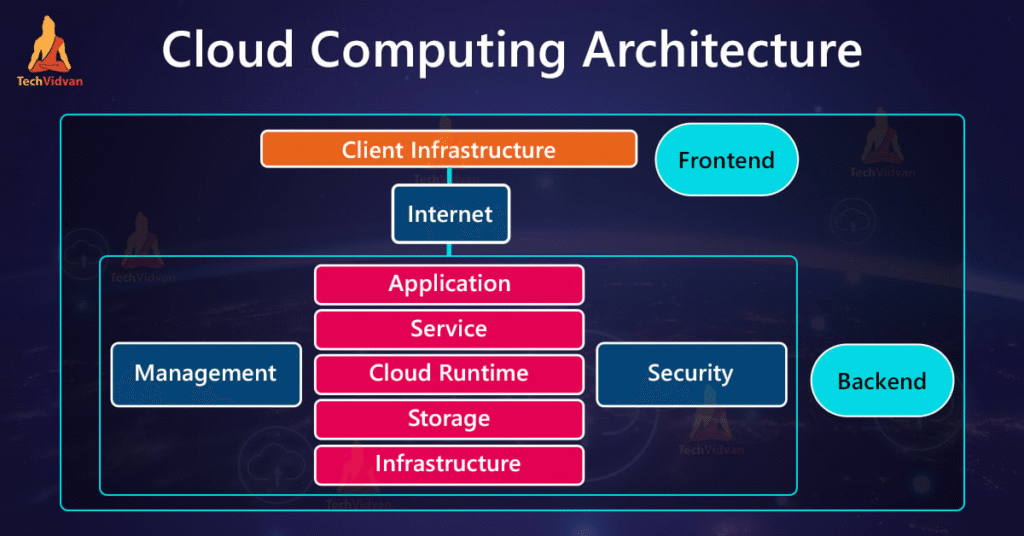
Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and sub-components required for cloud services. It can be divided into:
1. Front-End (Client-Side)
- User interface accessed via a web browser or app.
- Examples: Web portals, mobile apps, thin clients.
2. Back-End (Server-Side)
- Includes servers, storage, databases, and applications running in the cloud.
- Managed by cloud providers.
3. Cloud Delivery Models
- The three service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS).
4. Cloud Management
- Security, load balancing, scaling, and monitoring handled by cloud providers.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Cost-efficient (no upfront infrastructure cost)
- Scalability (resources can expand or shrink as needed)
- Accessibility (anywhere, anytime, with internet)
- Reliability (data backups and disaster recovery)
- Collaboration (multiple users can work on the same resource)
Challenges of Cloud Computing
- Security risks (data stored on external servers)
- Downtime (internet dependency)
- Limited control (provider manages infrastructure)
- Vendor lock-in (difficult to migrate between providers)
Applications of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is used in almost every field today.
- Education: Online learning platforms (Coursera, Google Classroom).
- Entertainment: Video streaming (Netflix, YouTube).
- Business: CRM, HR, and data analytics software.
- Healthcare: Patient data storage and analysis.
- Engineering: Big data processing, AI, and IoT applications.
Cloud Computing Cheatsheet (Quick Revision Notes)
- Cloud computing = Internet-based computing services.
- Service Models = IaaS, PaaS, SaaS.
- Deployment Models = Public, Private, Hybrid, Community.
- Key Features = On-demand, scalable, pay-as-you-go.
- Architecture = Front-end + Back-end + Delivery models.
- Benefits = Cost savings, scalability, accessibility.
- Challenges = Security, downtime, vendor lock-in.

FAQ – Cloud Computing Cheatsheet
Q1. What is cloud computing in simple words?
Cloud computing means using the internet to access servers, storage, and applications instead of owning physical hardware.
Q2. What are the 3 main types of cloud services?
IaaS (infrastructure), PaaS (platform), SaaS (software).
Q3. Which cloud deployment model is most common?
The public cloud is the most widely used because it is cost-effective and easily accessible.
Q4. Is cloud computing important for BTech exams?
Yes, cloud computing is part of Computer Science/IT syllabi and often asked in exams and placements.
Q5. What are some real-life examples of cloud computing?
Google Drive, Netflix, Gmail, Microsoft Azure, AWS.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is a revolutionary technology that powers today’s digital world. For BTech students, it’s an essential topic to master for both academic success and career readiness.
By remembering the service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), deployment models, and architecture, you’ll be able to answer exam questions confidently and also demonstrate technical knowledge in interviews.
Keep this Cloud Computing Cheatsheet handy for last-minute revisions.
Author Profile
- At Learners View, we're passionate about helping learners make informed decisions. Our team dives deep into online course platforms and individual courses to bring you honest, detailed reviews. Whether you're a beginner or a lifelong learner, our insights aim to guide you toward the best educational resources available online.
Latest entries
 UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes
UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)
UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)







