Software Engineering Cheatsheet – SDLC Models, UML Diagrams
Introduction
Software Engineering is one of the core subjects in Computer Science and IT engineering courses. Whether you are preparing for semester exams, placements, or project work, having a concise cheatsheet saves time and makes revision easier.
In this article, we bring you a Software Engineering Cheatsheet covering:
- The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) models.
- The most important UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagrams.
- Key concepts that frequently appear in exams and viva questions.
If you are a BTech student, this will serve as a quick revision guide to strengthen your fundamentals in software engineering.
What is Software Engineering?
Software Engineering is the disciplined approach of designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software systems. It applies engineering principles to software development to ensure reliability, maintainability, and scalability.
Key Objectives of Software Engineering:
- Develop high-quality software.
- Reduce cost and time of development.
- Ensure the software meets user requirements.
- Improve maintainability and scalability of applications.
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
The SDLC defines the process of developing software systematically. It breaks down the development into well-defined phases to ensure clarity and quality.
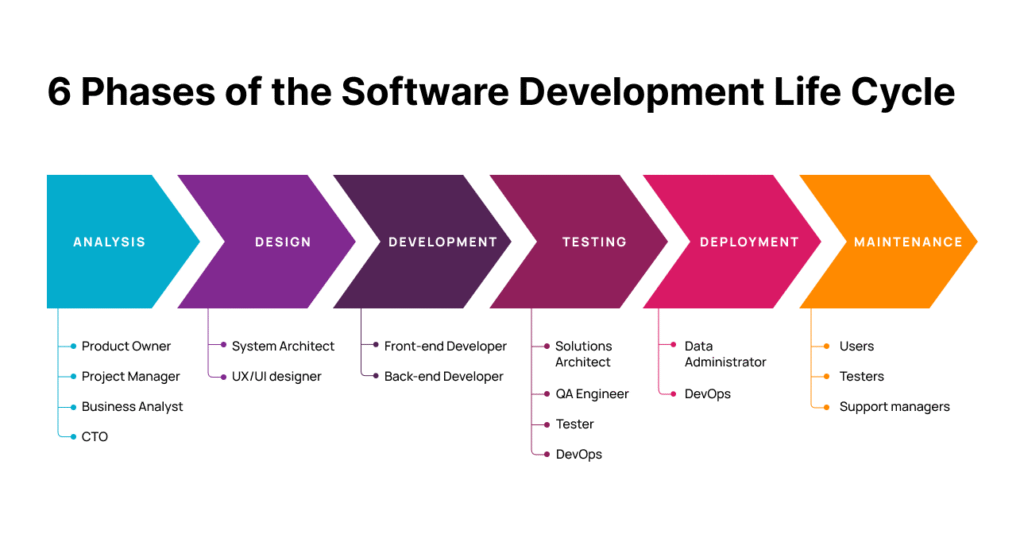
Phases of SDLC
- Requirement Analysis – Collecting and documenting user needs.
- System Design – Creating architecture and design specifications.
- Implementation (Coding) – Writing the actual code.
- Testing – Verifying and validating the software.
- Deployment – Delivering the software to users.
- Maintenance – Updating and fixing the software after release.
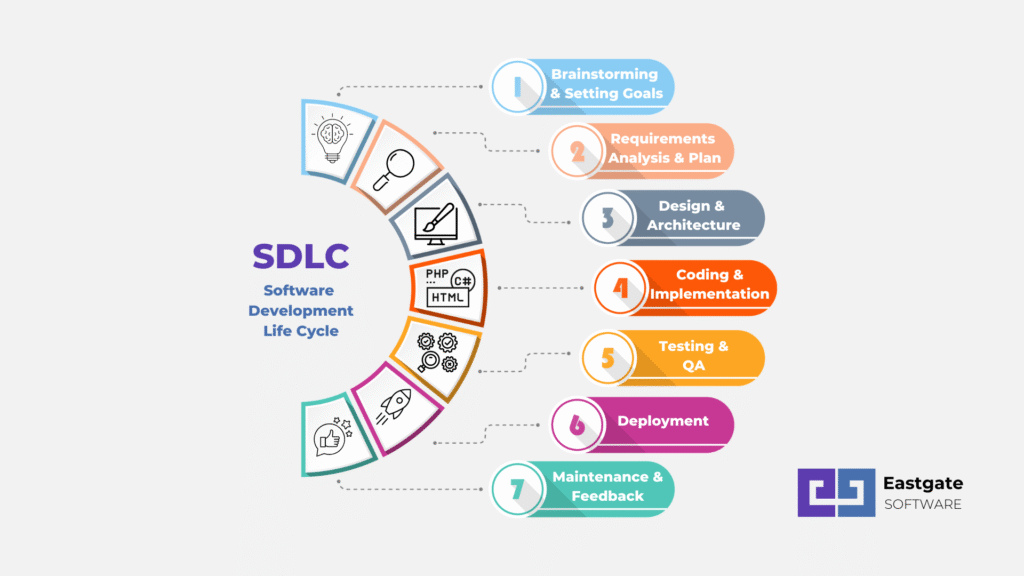
SDLC Models
There are several SDLC models, each with its advantages and limitations.
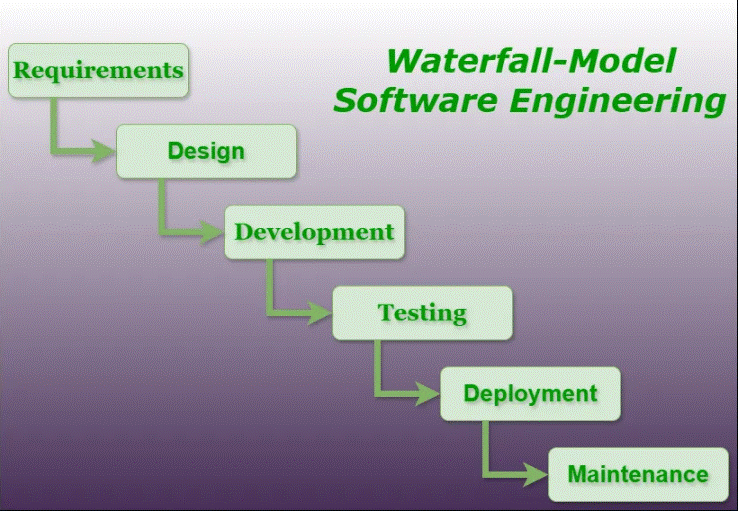
1. Waterfall Model
- Linear sequential flow: each phase must be completed before moving to the next.
- Best for projects with well-defined requirements.
Advantages:
- Simple to understand and manage.
- Easy for documentation.
Disadvantages:
- Inflexible; hard to go back once a phase is completed.
- Not suitable for projects with changing requirements.
2. Iterative Model
- The project is developed in small parts (iterations).
- Each iteration adds functionality until the final system is built.
Advantages:
- Early working version available.
- Easier to manage risks.
Disadvantages:
- Requires proper planning and design.
- May need more resources.
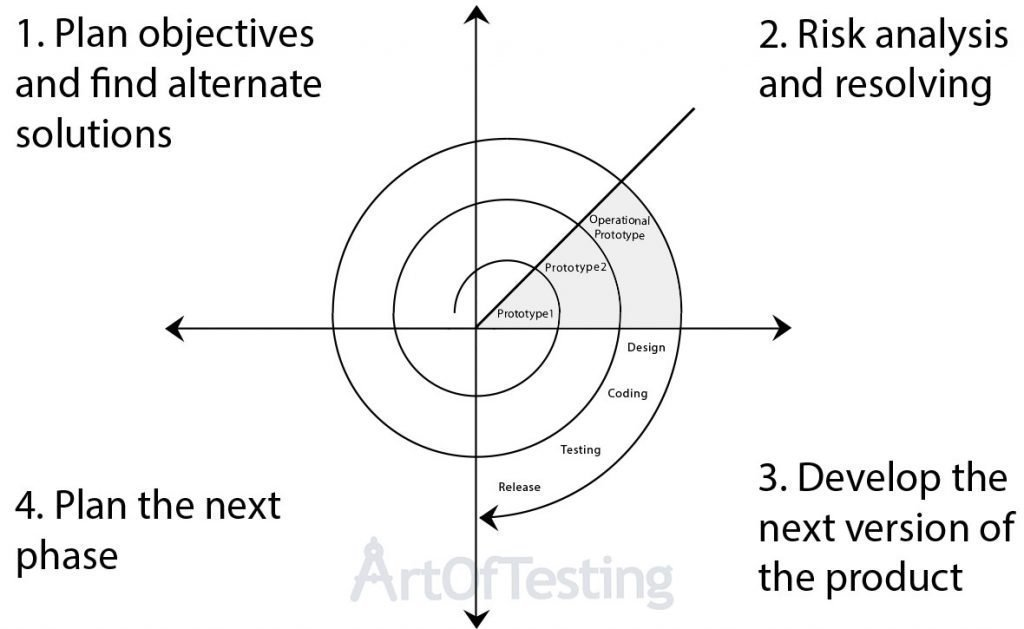
3. Spiral Model
- Combines iterative development with risk analysis.
- Each phase is repeated in a spiral until the software is complete.
Advantages:
- Best for large and complex projects.
- Risk management is strong.
Disadvantages:
- Expensive due to repeated phases.
- Complex to manage.
4. V-Model (Verification and Validation Model)
- An extension of the waterfall model with simultaneous testing.
- Each development phase is directly associated with a testing phase.
Advantages:
- Strong emphasis on testing.
- Clear milestones.
Disadvantages:
- Inflexible for changing requirements.
- Not ideal for small projects.
5. Agile Model
- Iterative and incremental approach.
- Focuses on flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback.
Advantages:
- Adapts to changes quickly.
- Delivers working software frequently.
Disadvantages:
- Requires experienced teams.
- Less documentation.
6. Big Bang Model
- Minimal planning; coding begins immediately.
- Best for small projects or research work.
Advantages:
- Simple and fast.
- Requires fewer resources in the beginning.
Disadvantages:
- High risk of failure.
- Not suitable for complex systems.
UML (Unified Modeling Language) in Software Engineering
UML is a standard way to visualize the design of a software system. It provides diagrams that help in understanding, designing, and documenting software systems.
Importance of UML:
- Standardized representation of software architecture.
- Improves communication among team members.
- Helps in both analysis and design phases.
Types of UML Diagrams
UML diagrams are broadly classified into Structural Diagrams and Behavioral Diagrams.
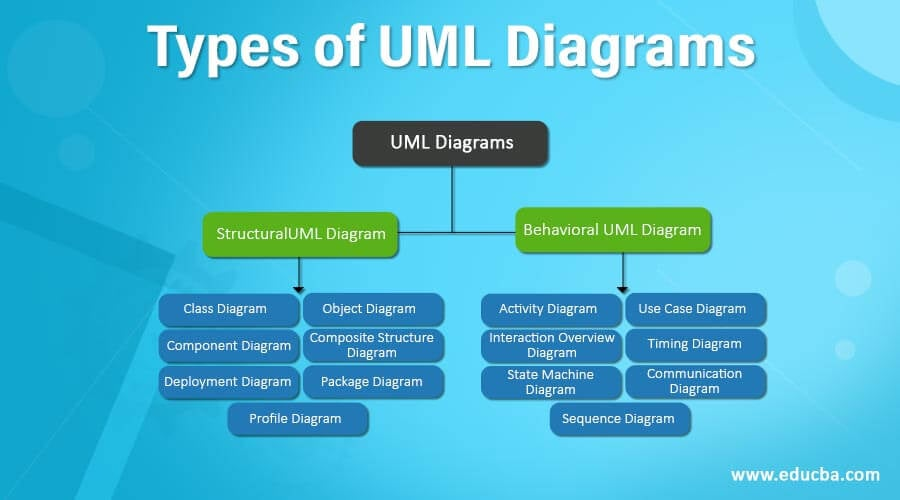
Structural Diagrams
- Class Diagram
- Shows classes, attributes, methods, and relationships.
- Useful for object-oriented design.
- Object Diagram
- Snapshot of object instances at a particular time.
- Demonstrates real examples of class relationships.
- Component Diagram
- Shows software components and dependencies.
- Useful for implementation view.
- Deployment Diagram
- Shows physical deployment of software on hardware.
- Useful in system architecture.
Behavioral Diagrams
- Use Case Diagram
- Represents user interactions with the system.
- Shows functional requirements.
- Sequence Diagram
- Shows object interactions in time sequence.
- Useful for dynamic behavior.
- Activity Diagram
- Represents workflows of activities.
- Similar to flowcharts.
- State Machine Diagram
- Represents states and transitions of objects.
- Useful for event-driven systems.
- Communication Diagram
- Focuses on object interactions using messages.
- Alternative to sequence diagrams.
Cheatsheet Summary
Here’s a quick revision summary:
- SDLC Models: Waterfall, Iterative, Spiral, V-Model, Agile, Big Bang.
- Key UML Diagrams: Class, Object, Component, Deployment, Use Case, Sequence, Activity, State Machine, Communication.
- Exam Tip: Focus on advantages and disadvantages of each SDLC model and purpose of each UML diagram.
FAQs – Software Engineering Cheatsheet
Q1. What is the most commonly used SDLC model today?
Agile is the most widely used model due to its flexibility and adaptability to changes.
Q2. Which UML diagrams are most important for exams?
Class diagrams, use case diagrams, sequence diagrams, and activity diagrams are the most frequently asked in exams.
Q3. How is the V-Model different from the Waterfall Model?
The V-Model integrates testing with each phase, while the Waterfall Model performs testing only after development is complete.
Q4. Why is UML important in software design?
UML provides a standard visualization that helps in communication, documentation, and effective design of systems.
Q5. Which SDLC model is best for large projects?
The Spiral model is preferred for large, complex, and high-risk projects due to its risk management approach.
Conclusion
Software Engineering is all about building software systematically and efficiently. The SDLC models provide structured approaches to development, while UML diagrams help in visualizing system design.
This cheatsheet gives you a concise revision guide for exams, viva, and placements. Focus on understanding the flow of SDLC and the purpose of UML diagrams to quickly answer questions in your exams.
Author Profile
- At Learners View, we're passionate about helping learners make informed decisions. Our team dives deep into online course platforms and individual courses to bring you honest, detailed reviews. Whether you're a beginner or a lifelong learner, our insights aim to guide you toward the best educational resources available online.
Latest entries
 UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes
UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)
UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)