Microprocessor & Microcontroller Cheatsheet – 8085, 8051 Basics
Introduction
Engineering exams often test your understanding of microprocessors (8085) and microcontrollers (8051). While textbooks are detailed, they can feel overwhelming when you need quick revision before exams or viva. That’s why we created this Microprocessor & Microcontroller Cheatsheet—a simplified, scannable guide covering the most important points.
Here, you’ll find:
- Core concepts of 8085 microprocessor and 8051 microcontroller
- Architecture overview with block diagrams
- Instruction sets and addressing modes
- Key differences between microprocessor and microcontroller
- Most asked viva and exam points
By the end, you’ll have a ready-to-revise, exam-focused cheatsheet to save time and boost your confidence.
Basics of Microprocessors and Microcontrollers
What is a Microprocessor?
- A microprocessor is the brain of a computer system—a general-purpose CPU on a single chip.
- It performs arithmetic and logic operations, manages instructions, and controls system operations.
- Requires external memory, input/output devices, and peripheral support to work.
Example: Intel 8085 (8-bit), Intel 8086 (16-bit).
What is a Microcontroller?
- A microcontroller is a system on a chip (SoC) containing CPU, memory, and I/O ports.
- Designed for specific control applications like washing machines, automobiles, or embedded systems.
- Reduces cost, space, and power consumption.
Example: Intel 8051, PIC, ARM-based microcontrollers.
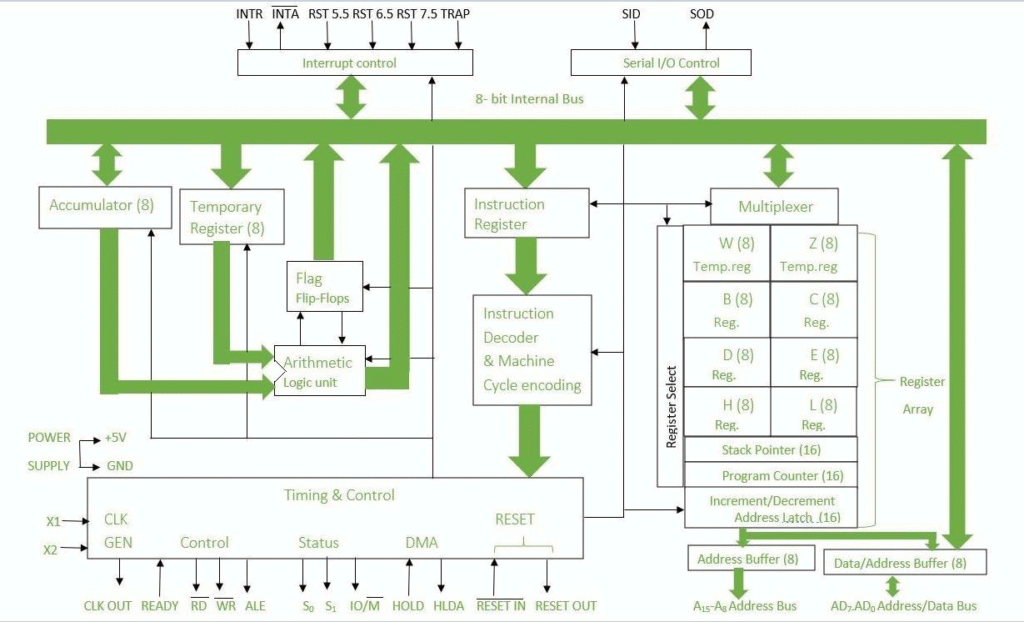
8085 Microprocessor Cheatsheet
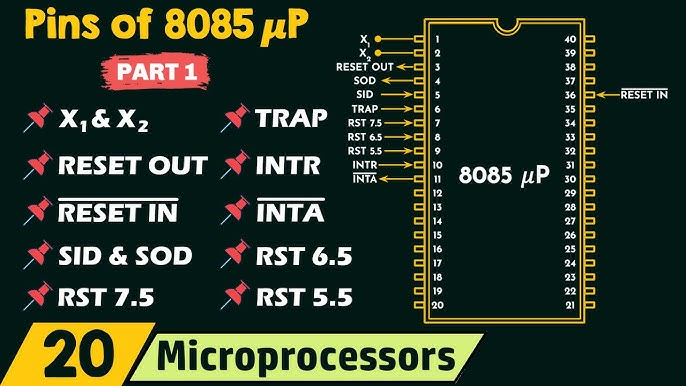
Key Features of 8085
- 8-bit processor, 74 instructions, 246 opcodes.
- Operates at 3 MHz (typical).
- Requires external memory (up to 64 KB).
- 40-pin IC.
8085 Architecture (Quick Points)
- Registers: Accumulator (A), B, C, D, E, H, L, Program Counter (PC), Stack Pointer (SP).
- ALU: Performs arithmetic & logic operations.
- Control Unit: Manages fetching & decoding.
- Instruction Register: Holds current instruction.
- Timing & Control Signals: ALE, RD, WR, etc.
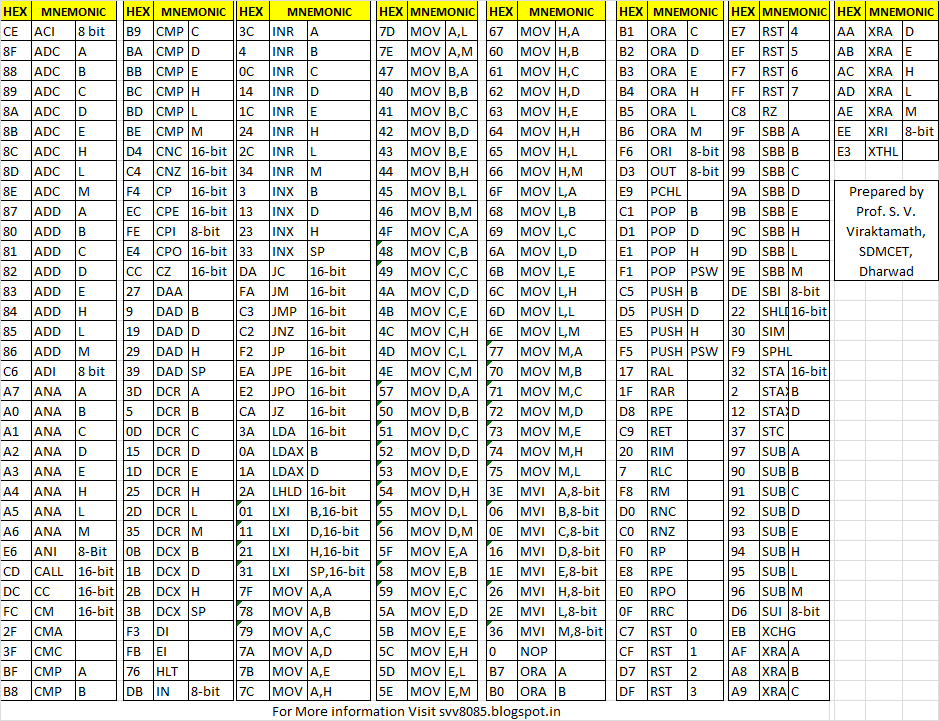
Instruction Set of 8085
- Data Transfer: MOV, MVI, LDA, STA, LHLD
- Arithmetic: ADD, SUB, INR, DCR, ADI, SUI
- Logical: ANA, XRA, ORA, CMP
- Branching: JMP, JNZ, JC, CALL, RET
- Control: NOP, HLT, DI, EI
Addressing Modes in 8085
- Immediate Addressing – Operand is part of instruction (e.g., MVI A, 32H).
- Register Addressing – Operand in register (e.g., MOV A, B).
- Direct Addressing – Memory address specified directly (e.g., LDA 2050H).
- Indirect Addressing – Address stored in register pair (e.g., MOV A, M).
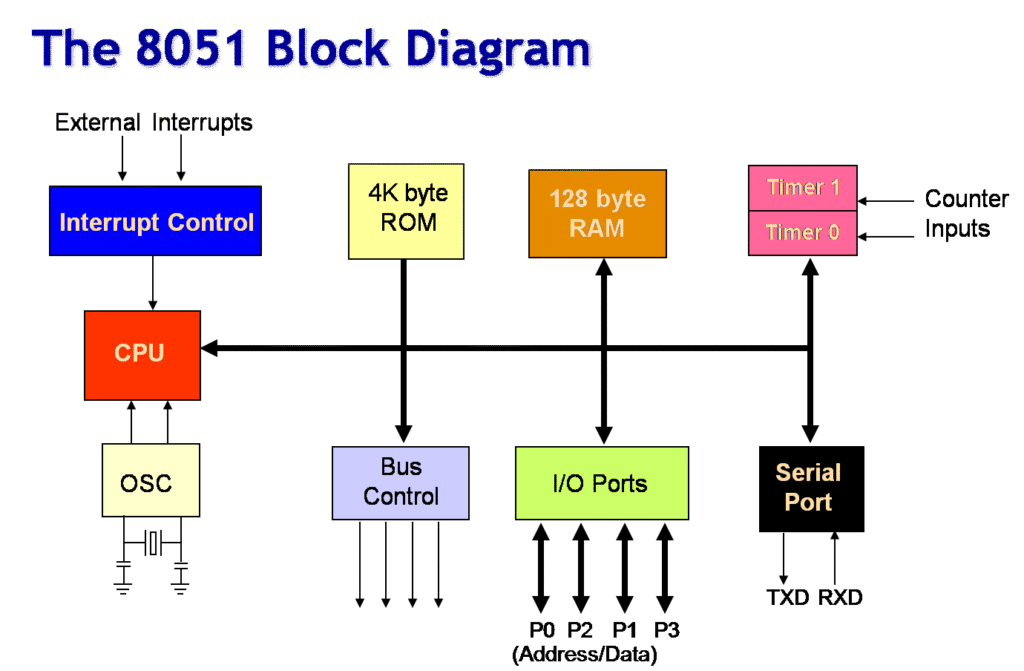
8051 Microcontroller Cheatsheet
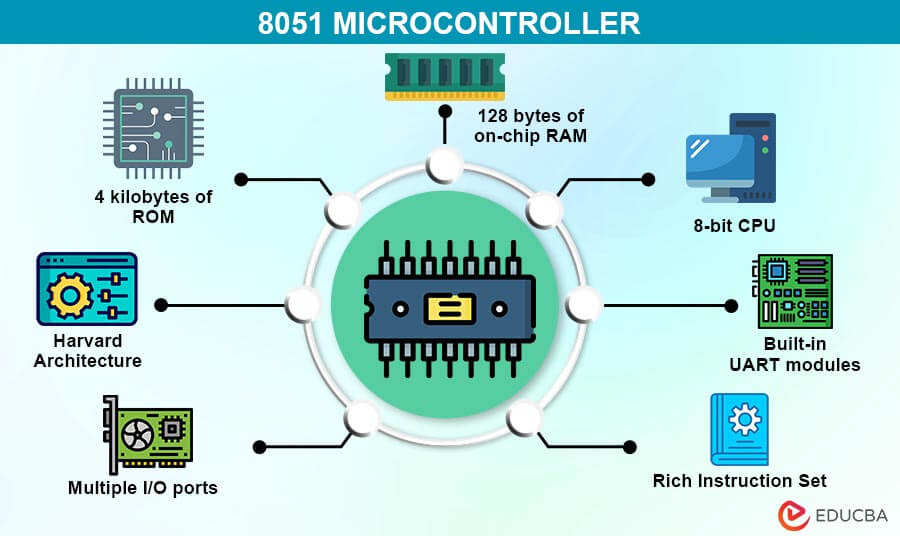
Key Features of 8051
- 8-bit CPU with 128 bytes internal RAM & 4 KB ROM.
- Four 8-bit I/O ports.
- Two 16-bit timers/counters.
- Serial communication support (UART).
- 40-pin IC.
8051 Architecture (Quick Points)
- Registers: Accumulator (A), B register, DPTR (Data Pointer), Program Counter (PC).
- Memory Organization:
- 4 KB ROM (program memory).
- 128 bytes RAM (data memory).
- Special Function Registers (SFRs).
- I/O Ports: P0, P1, P2, P3.
- Timers: For delay generation & counting events.
Instruction Set of 8051
- Data Transfer: MOV, PUSH, POP, XCH
- Arithmetic: ADD, SUBB, MUL, DIV, INC, DEC
- Logical: ANL, ORL, CPL, CLR, RL, RR
- Branching: SJMP, LJMP, AJMP, CALL, RET
- Bit Manipulation: SETB, CLR, JNB
Addressing Modes in 8051
- Immediate – MOV A, #55H
- Register – MOV A, R0
- Direct – MOV A, 40H
- Indirect – MOV A, @R0
- Indexed – MOVC A, @A+DPTR
[YOUTUBE VIDEO PLACEHOLDER — Search YouTube for: “8051 microcontroller tutorial for beginners”]
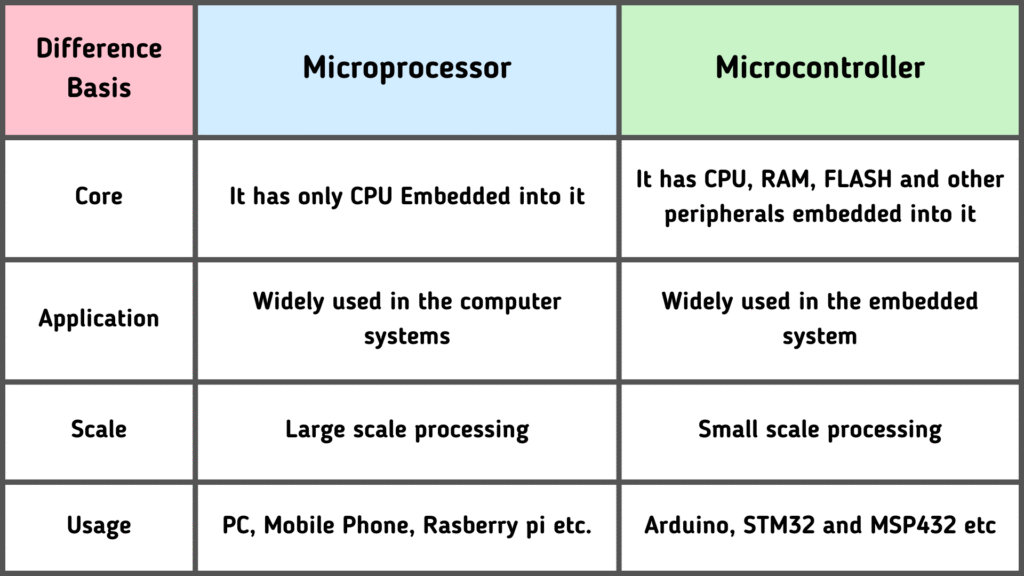
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller – Key Differences
| Feature | Microprocessor (8085) | Microcontroller (8051) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | General-purpose CPU | System on a chip (CPU + Memory + I/O) |
| Memory | External required | Built-in ROM & RAM |
| I/O Ports | External needed | Inbuilt I/O ports |
| Cost | Higher (needs peripherals) | Lower (integrated) |
| Applications | Computers, servers | Embedded systems, appliances |
Common Viva Questions
- What is the difference between 8085 and 8051?
- Why does 8085 need external memory?
- What are the addressing modes of 8051?
- Explain flag registers in 8085.
- Give real-life applications of microcontrollers.
6. Quick Revision Notes
- 8085 is a microprocessor (CPU only), 8051 is a microcontroller (CPU + Memory + I/O).
- 8085 has 74 instructions; 8051 has bit-level instructions.
- 8085 focuses on computation; 8051 focuses on control applications.
- Both are 8-bit, but differ in integration and purpose.
FAQs
Q1. What is the main difference between 8085 and 8051?
8085 is a general-purpose microprocessor that requires external memory and peripherals, while 8051 is a microcontroller with built-in memory and I/O ports designed for embedded control applications.
Q2. Why is 8085 called an 8-bit processor?
Because it processes 8 bits of data at a time and has an 8-bit data bus.
Q3. Which is easier for beginners — 8085 or 8051?
8051 is easier to learn for embedded applications, while 8085 is better for understanding the fundamentals of microprocessor operations.
Q4. What are real-world applications of 8051 microcontroller?
Used in washing machines, automobiles, robotics, medical devices, and industrial automation systems.
Q5. Can 8085 be used in modern systems?
Rarely. It’s mostly used in educational labs and basic computing demonstrations. Modern systems use advanced processors or microcontrollers.
Conclusion
This Microprocessor & Microcontroller Cheatsheet (8085 & 8051 Basics) is designed to give you quick, exam-ready revision without going through lengthy textbooks. If you’re preparing for BTech exams, viva, or placements, this guide will help you answer questions confidently.
For deeper preparation, explore our Engineering Cheatsheets library with formula sheets, quick notes, and placement prep material.
Author Profile
- At Learners View, we're passionate about helping learners make informed decisions. Our team dives deep into online course platforms and individual courses to bring you honest, detailed reviews. Whether you're a beginner or a lifelong learner, our insights aim to guide you toward the best educational resources available online.
Latest entries
 UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes
UncategorizedOctober 3, 2025AKTU BTech Important Questions & Notes Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 24, 2025C++ Programming Cheatsheet – STL, OOP Concepts, Syntax Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions
Exam Revision NotesSeptember 22, 2025Java Programming Cheatsheet – Collections, OOP, Exceptions UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)
UncategorizedAugust 28, 2025BTech 1st Year Notes & Cheatsheets (Subject-Wise)